TASK BASED LANGUAGE TEACHING
What is Task-Based Language Teaching?
Theory of language
- Language is primarily a means of making meaning: TBLT considers meaning as a central focal point in language teaching. The approach is concerned with the outcome of tasks.
- Multiple models of language inform task-based instruction: Structural, functional and interactional models influence TBLT adherents.
- Lexical units are central in language use and language learning: TBLT considers vocabulary items to include not only individual words but also phrases, sentence frames, collocations and prefabricated routines.
- “Conversation” is the central focus of language and the keystone of language acquisition: Learners are required to produce and understand communicative messages. That is exchanging information is crucial to language acquisition.
Theory of learning
- Tasks provide both the input and output processing necessary for language acquisition: If Krashen stresses the importance of comprehensible input, TBLT advocates have argued that comprehensible output is also of equal importance.
- Task activity and achievement are motivational: Tasks appeal to learners’ learning styles and may involve physical activity, collaboration, and partnership.
- Learning difficulty can be negotiated and fine-tuned for a particular pedagogical purpose: Tasks may be designed in such a way that they meet learners’ level of proficiency. That is, providing the appropriate target input is crucial to facilitate language acquisition.
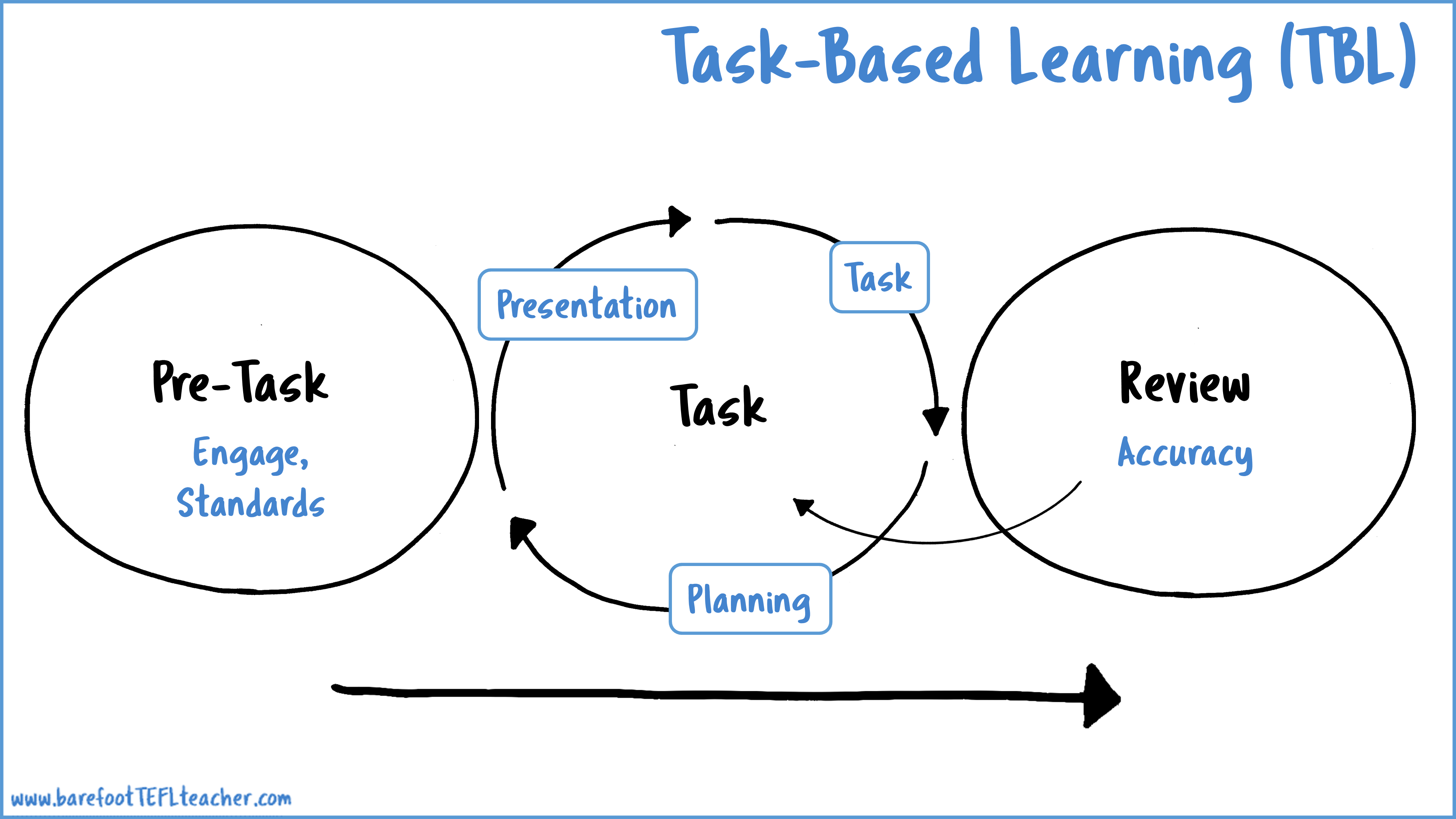
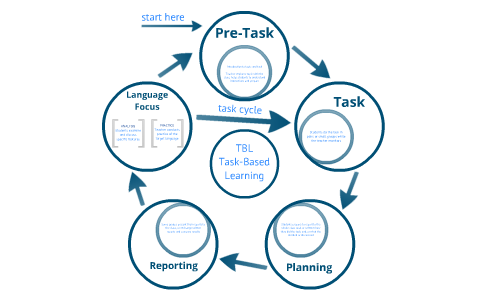
TASK
Task type
-Real world
-PedagogicalReal world
- Psycholinguistic- Needs analysisPedagogical
-Test-SLA theory / researchAdvantages of TBLT
Implicit learning
The aim of TBLT is to help learners develop implicit knowledge of the language that will enable them to participate easily and naturally in communication. The learners get the form and use of the target language without being explicitly being taught. The role of the teacher is to design tasks by replicating and creating the conditions for language learning and for communication that exists outside the confines of the classroom. The aim is that the learners’ interlanguage will gain implicit language knowledge while doing tasks.
Incidental learning
Much of our everyday learning is incidental. TBLT provides opportunities for unplanned learning. Completing a real-world task allows the acquisition to take place without any deliberate intention on the part of the learner or the teacher.
Meaningful learning
TBLT allows meaningful communication to occur during the accomplishment of tasks.
Disadvantages of TBLT
- Some teachers criticize TBLT for focusing mainly on fluency at the expense of accuracy.
- TBLT requires a high level of creativity and initiative on the part of the teacher.
- TBLT requires resources beyond the textbooks and related materials usually found in language classrooms.
- Evaluation of task-based instruction can be difficult. The nature of task-based learning does not allow it to be objectively measurable.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario